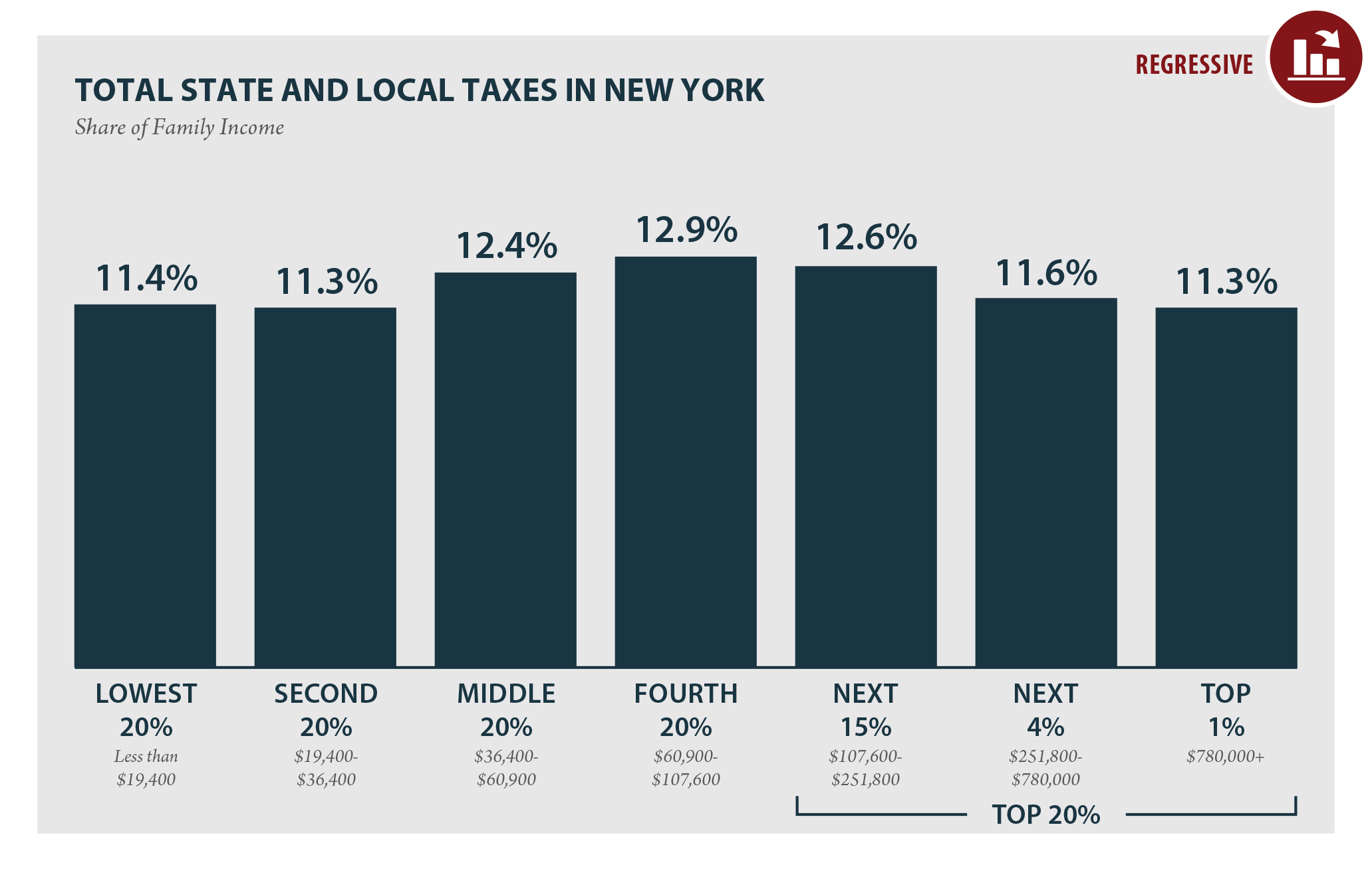
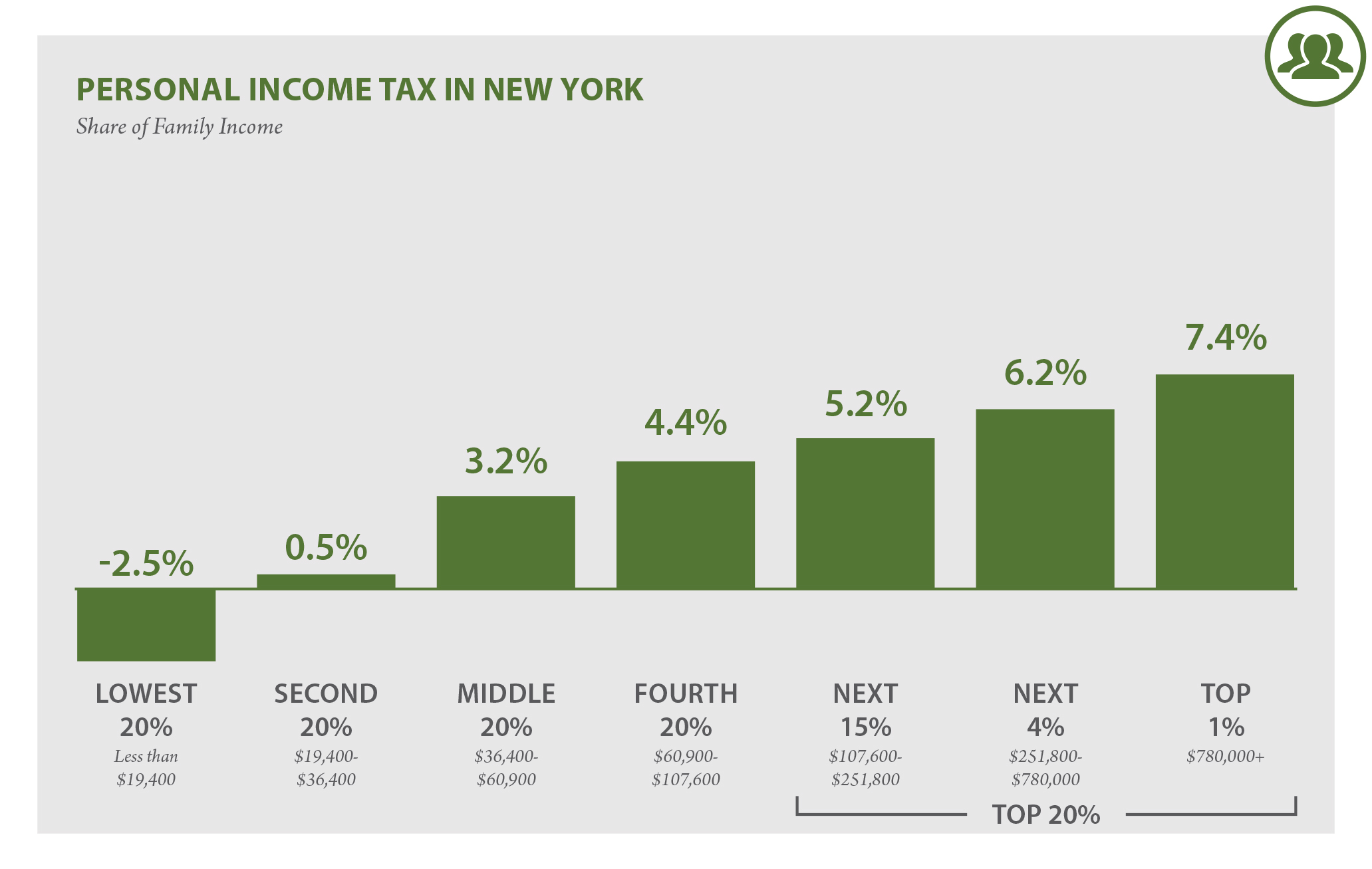
Understanding New York State income tax rates is crucial for residents and businesses alike, as it directly impacts their financial planning and tax obligations. The state's tax structure is designed to ensure fairness while generating revenue for public services. Whether you're a first-time filer or a seasoned taxpayer, having a clear grasp of these rates can help you make informed decisions.
New York State income tax rates vary based on income levels, with progressive brackets ensuring that individuals and families pay according to their ability. This system aims to balance the state's fiscal needs with the financial well-being of its residents. In this article, we will delve into the details of these tax rates, explore how they are calculated, and provide actionable insights for taxpayers.
As tax laws and regulations evolve, staying updated is essential. This guide will cover the latest New York State income tax rates, exemptions, deductions, and credits, ensuring you have all the information you need to navigate the tax season confidently.
Read also:Solofa Fatu A Rising Star In The World Of Arts And Entertainment
Table of Contents
- Overview of New York State Income Tax Rates
- The Progressive Tax System in New York
- Understanding Tax Brackets and Marginal Rates
- Filing Status and Its Impact on Tax Rates
- Key Deductions and Exemptions
- Tax Credits Available in New York State
- Biennial Updates to Tax Rates
- New York State Taxes for Businesses
- Federal vs. State Income Taxes
- Tax Planning Strategies for Residents
Overview of New York State Income Tax Rates
New York State income tax rates are structured to reflect the state's commitment to equitable taxation. As of 2023, the state employs a progressive tax system, meaning that higher income levels are taxed at higher rates. This approach ensures that taxpayers contribute proportionally to the state's revenue.
The current tax brackets range from 4% for the lowest income bracket to 10.9% for the highest. These rates apply to both individuals and married couples filing jointly. Additionally, New York City residents and Yonkers residents face an additional local tax, further impacting their overall tax liability.
Understanding these rates is vital for accurate tax preparation and compliance. By familiarizing yourself with the brackets and their implications, you can better anticipate your tax obligations and plan accordingly.
The Progressive Tax System in New York
How Progressive Taxation Works
New York's progressive tax system divides income into brackets, each taxed at a different rate. For example, if your income falls into multiple brackets, only the portion of income within each bracket is taxed at that rate. This method prevents taxpayers from being disproportionately affected by higher rates.
- Bracket 1: 4% for income up to $8,500
- Bracket 2: 4.5% for income between $8,501 and $11,700
- Bracket 3: 5.25% for income between $11,701 and $25,000
This structure ensures that lower-income individuals pay a smaller percentage of their income compared to higher-income earners, promoting economic fairness.
Understanding Tax Brackets and Marginal Rates
Tax brackets in New York State determine the percentage of income taxed at each level. The marginal tax rate applies only to the income within that specific bracket, not the entire income. For instance, if you earn $50,000 annually, the first $8,500 is taxed at 4%, the next portion at 4.5%, and so on.
Read also:Did Michael Jackson Perform At A Super Bowl Unveiling The Truth Behind The Iconic Performance
Knowing your tax bracket helps you estimate your tax liability and plan for deductions and credits. It also allows you to assess the impact of potential income changes on your tax bill.
Filing Status and Its Impact on Tax Rates
Types of Filing Status
Your filing status significantly affects your New York State income tax rates. The four primary statuses are Single, Married Filing Jointly, Married Filing Separately, and Head of Household. Each status has different income thresholds and tax brackets.
- Single: Applicable to individuals who are unmarried or legally separated.
- Married Filing Jointly: Allows couples to combine their incomes and file a single return.
- Married Filing Separately: Provides an option for couples to file individual returns.
- Head of Household: Designed for single taxpayers supporting dependents.
Selecting the correct filing status ensures you take full advantage of applicable deductions and credits.
Key Deductions and Exemptions
New York State offers various deductions and exemptions to reduce taxable income. These include personal exemptions, dependent exemptions, and itemized deductions. Taxpayers can choose between the standard deduction or itemizing their deductions, depending on which provides greater tax savings.
For instance, the standard deduction for single filers in 2023 is $8,900, while married couples filing jointly can claim $17,800. Itemized deductions may include mortgage interest, charitable contributions, and state and local taxes (SALT).
Tax Credits Available in New York State
Popular Tax Credits
Tax credits directly reduce the amount of tax owed, making them valuable for taxpayers. New York State offers several credits, including:
- Child Tax Credit: Provides relief for taxpayers with dependents.
- Elderly and Disabled Credit: Benefits senior citizens and individuals with disabilities.
- Homestead Credit: Reduces property taxes for eligible homeowners.
Claiming these credits can significantly lower your tax liability and improve your financial situation.
Biennial Updates to Tax Rates
New York State regularly updates its income tax rates to align with economic conditions and legislative changes. These updates often occur biennially, ensuring the tax system remains current and effective. Taxpayers should stay informed about these updates to avoid underpayment or overpayment of taxes.
For example, the 2023 updates introduced minor adjustments to the tax brackets, reflecting inflation and cost-of-living increases. Staying updated helps taxpayers adapt to changes and maintain compliance.
New York State Taxes for Businesses
Corporate Income Tax Rates
In addition to individual income taxes, New York State imposes corporate income taxes on businesses operating within the state. The corporate tax rate is currently 6.5%, with additional surcharges for high-income corporations. Businesses must also consider local taxes and industry-specific regulations.
Understanding these taxes is crucial for business owners and financial planners. Proper tax planning can optimize profitability and ensure compliance with state regulations.
Federal vs. State Income Taxes
While New York State income tax rates focus on state-level obligations, federal income taxes also play a significant role in a taxpayer's overall liability. The federal tax system operates independently but often intersects with state taxes, particularly through the SALT deduction.
Taxpayers should consider both federal and state taxes when preparing their returns. Coordinating these obligations ensures comprehensive compliance and maximizes available deductions and credits.
Tax Planning Strategies for Residents
Maximizing Savings and Compliance
Effective tax planning involves understanding New York State income tax rates and leveraging available deductions and credits. Strategies include:
- Timing income and deductions to optimize tax brackets.
- Utilizing retirement accounts to defer taxable income.
- Claiming all eligible credits and exemptions.
By implementing these strategies, taxpayers can minimize their tax liability while ensuring compliance with state and federal regulations.
Kesimpulan
New York State income tax rates play a critical role in the financial lives of residents and businesses. Understanding the progressive tax system, tax brackets, filing statuses, deductions, and credits empowers taxpayers to make informed decisions. Staying updated with biennial updates and coordinating federal and state taxes further enhances tax planning efforts.
We encourage you to apply the insights gained from this guide to your tax preparation process. If you have questions or need further clarification, please leave a comment or explore additional resources on our website. Together, we can ensure a smoother and more efficient tax season for everyone.