New York State income tax brackets play a crucial role in determining how much tax residents owe each year. Whether you're a new resident, a long-time New Yorker, or simply trying to understand the intricacies of state taxes, having a solid grasp of the tax brackets is essential. This article will provide you with an in-depth understanding of the New York State income tax brackets, ensuring you're well-prepared for tax season.
Understanding the New York State income tax system can be complex, but it doesn't have to be overwhelming. By breaking down the tax brackets and explaining how they work, you'll be able to make informed financial decisions. This guide aims to simplify the process and provide clarity on how much you might owe based on your income level.
As we delve deeper into the topic, we'll explore the latest updates for 2023, discuss how the tax brackets affect different income levels, and offer practical tips to help you optimize your tax planning. Let's get started!
Read also:Understanding The Caveat Meaning A Comprehensive Guide
Table of Contents
- Introduction to New York State Income Tax Brackets
- Current Tax Brackets for 2023
- How Tax Brackets Work
- Factors Affecting Tax Brackets
- Deductions and Credits
- Comparison with Federal Tax
- Tips for Tax Planning
- Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Resources for Taxpayers
- Conclusion and Next Steps
Introduction to New York State Income Tax Brackets
New York State income tax brackets are designed to ensure that individuals pay taxes in proportion to their income. This progressive tax system means that higher earners contribute a larger percentage of their income compared to those with lower earnings. The state government regularly updates these brackets to reflect economic changes and inflation.
Why Understanding Tax Brackets Matters
Knowing your tax bracket is critical for accurate tax planning. It allows you to estimate your tax liability and make adjustments to your withholdings if necessary. Additionally, understanding the brackets can help you identify potential deductions and credits that may reduce your taxable income.
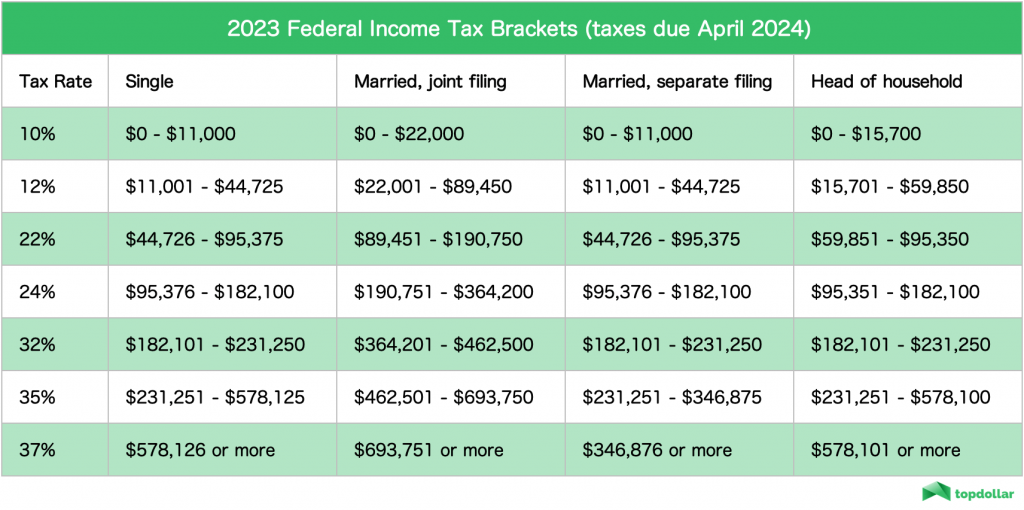
Current Tax Brackets for 2023
In 2023, New York State has six distinct tax brackets, each with its own marginal tax rate. These brackets are adjusted annually for inflation, ensuring they remain fair and up-to-date. Below is a breakdown of the current tax brackets:
- Up to $8,650: 4%
- $8,651 to $11,950: 4.5%
- $11,951 to $24,250: 5.25%
- $24,251 to $253,900: 5.99%
- $253,901 to $1,087,000: 6.23%
- Above $1,087,000: 8.82%
How These Rates Impact Taxpayers
Each bracket represents a range of income taxed at a specific rate. For example, if your income falls into the highest bracket, only the portion of your income above $1,087,000 is taxed at 8.82%. The rest is taxed at lower rates according to the applicable brackets.
How Tax Brackets Work
The New York State income tax system uses marginal tax rates, meaning that only the portion of your income falling within a specific bracket is taxed at that rate. This ensures that taxpayers are not penalized for earning more money.
Example Calculation
Let's say you earn $50,000 annually. Here's how your tax liability would be calculated:
Read also:Nashville Chic Your Ultimate Guide To Stylish Nashville Outfit Inspiration
- $8,650 at 4% = $346
- $3,300 ($11,950 - $8,650) at 4.5% = $148.50
- $12,300 ($24,250 - $11,950) at 5.25% = $645.75
- $25,750 ($50,000 - $24,250) at 5.99% = $1,542.42
Total tax owed: $2,682.67
Factors Affecting Tax Brackets
Several factors influence which tax bracket you fall into. These include:
- Filing status (single, married filing jointly, etc.)
- Income level
- Dependents and deductions
Impact of Filing Status
Your filing status can significantly affect your tax bracket. For instance, married couples filing jointly often benefit from higher thresholds before moving into higher tax brackets.
Deductions and Credits
Taking advantage of deductions and credits can lower your taxable income and reduce your overall tax burden. Some common deductions include:
- Standard deduction
- Itemized deductions (e.g., mortgage interest, charitable contributions)
Credits, such as the Earned Income Tax Credit (EITC), can further decrease your tax liability. Be sure to consult with a tax professional to ensure you're claiming all eligible deductions and credits.
Standard Deduction vs. Itemized Deductions
Choosing between the standard deduction and itemized deductions depends on your individual circumstances. If your itemized deductions exceed the standard amount, it may be more beneficial to itemize.
Comparison with Federal Tax
While New York State income tax brackets are similar to federal tax brackets in structure, the rates and thresholds differ. It's important to consider both state and federal taxes when planning your finances. For example, the federal top tax rate is 37%, compared to New York's highest rate of 8.82%.
Key Differences
One key difference is the availability of certain deductions and credits at the state level that may not exist federally, and vice versa. Understanding these distinctions can help you optimize your tax strategy.
Tips for Tax Planning
Effective tax planning involves more than just understanding tax brackets. Here are some tips to help you minimize your tax liability:
- Contribute to retirement accounts (e.g., 401(k), IRA)
- Maximize eligible deductions and credits
- Consult with a tax advisor for personalized advice
Retirement Contributions
Contributing to retirement accounts not only helps secure your financial future but can also reduce your taxable income. Many retirement plans offer tax-deferred growth, allowing your investments to grow without immediate tax implications.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Mistakes during tax season can lead to unnecessary complications and penalties. Here are some common errors to avoid:
- Not reporting all sources of income
- Missing deadlines for filing and payment
- Overlooking available deductions and credits
Importance of Accuracy
Accuracy is paramount when filing your taxes. Double-check all figures and ensure you've included all necessary documentation. If unsure, seek assistance from a qualified tax professional.
Resources for Taxpayers
Several resources are available to help New York State taxpayers navigate the tax system:
- New York State Department of Taxation and Finance website
- Tax preparation software (e.g., TurboTax, H&R Block)
- Local tax assistance programs
Using Online Tools
Online tools and resources can simplify the tax filing process. Many offer step-by-step guidance and ensure you don't miss any deductions or credits. Additionally, they often provide alerts for upcoming deadlines and important updates.
Conclusion and Next Steps
Understanding New York State income tax brackets is essential for effective tax planning. By familiarizing yourself with the current brackets, taking advantage of deductions and credits, and avoiding common mistakes, you can minimize your tax liability and maximize your financial well-being.
We encourage you to take the following steps:
- Review your income and adjust withholdings as needed
- Explore available deductions and credits
- Consult with a tax professional for personalized advice
Feel free to leave a comment or share this article with others who may find it helpful. For more information on tax-related topics, explore our other articles on our website.