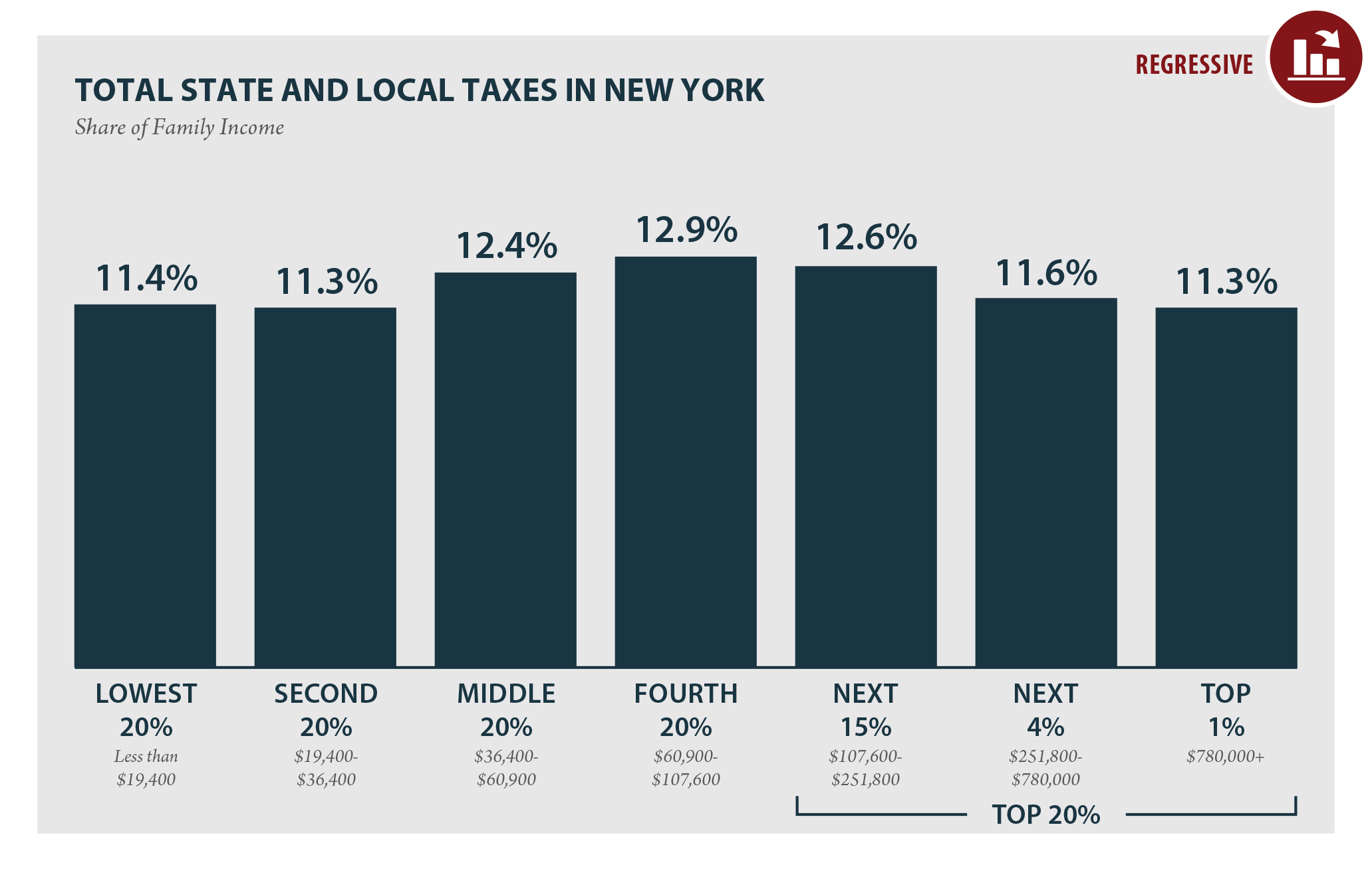
New York State income tax percentage is a crucial aspect of financial planning for residents. Understanding how the tax system works and the various brackets can significantly impact your annual budget. Whether you're a new resident or have lived in New York for years, staying informed about tax obligations is essential.
New York State imposes a progressive income tax system, meaning the tax rate increases as your income rises. This structure ensures that individuals with higher earnings contribute a larger percentage of their income. Knowing the specifics of these brackets can help you better manage your finances and plan for tax liabilities.
This article provides an in-depth analysis of New York State income tax percentages, including the latest updates, practical tips, and expert advice. By the end, you'll have a clearer understanding of how the system works and how to optimize your tax strategy.
Read also:Is Jayson Tatum White Unveiling The Truth Behind The Nba Stars Identity
Table of Contents
- Understanding New York State Income Tax
- New York State Income Tax Brackets
- Filing Status and Its Impact on Tax Rates
- Deductions and Credits in New York
- Amended Tax Returns
- Penalties for Late Payment
- Federal vs. State Tax Rates
- Using a New York State Tax Calculator
- Resources for Taxpayers
- Conclusion and Next Steps
Understanding New York State Income Tax
Overview of the Tax System
New York State income tax percentage is governed by a progressive tax system. This means that as your income increases, so does the percentage of tax you owe. The state tax rates are separate from federal tax rates, and residents must file both state and federal returns annually.
The New York State Department of Taxation and Finance oversees the collection and enforcement of income taxes. Residents are required to file their taxes by April 15th each year, unless an extension is granted.
New York State Income Tax Brackets
2023 Tax Brackets
As of 2023, New York State income tax brackets range from 4% to 10.90%. These brackets are adjusted annually to account for inflation and changes in the economy. Below is a breakdown of the current tax brackets:
- Taxable income up to $8,500: 4% tax rate
- $8,501 to $11,700: 4.5% tax rate
- $11,701 to $13,900: 5.25% tax rate
- $13,901 to $21,600: 5.97% tax rate
- $21,601 to $80,650: 6.09% tax rate
- $80,651 to $215,400: 6.33% tax rate
- $215,401 and above: 10.90% tax rate
These brackets apply to individuals filing as single or married filing separately. For married couples filing jointly, the brackets are adjusted accordingly.
Filing Status and Its Impact on Tax Rates
Choosing the Right Filing Status
Your filing status can significantly affect your New York State income tax percentage. The most common filing statuses include:
- Single
- Married Filing Jointly
- Married Filing Separately
- Head of Household
Each status has its own set of tax brackets and deductions. For example, married couples filing jointly often benefit from lower tax rates compared to filing separately.
Read also:Jonathan The Tortoise Exploring The Worlds Oldest Living Land Animal
Deductions and Credits in New York
Key Deductions and Credits
New York State offers several deductions and credits to help reduce your taxable income. Some of the most important ones include:
- Standard Deduction: Available to all taxpayers, this deduction reduces your taxable income by a fixed amount.
- Itemized Deductions: For those who qualify, itemized deductions can include mortgage interest, charitable contributions, and state and local taxes.
- Child Tax Credit: This credit provides relief for taxpayers with dependent children.
- Education Credits: Eligible taxpayers can claim credits for tuition and related expenses.
Utilizing these deductions and credits can lower your effective tax rate and increase your take-home pay.
Amended Tax Returns
When to File an Amended Return
If you discover an error on your original tax return, you may need to file an amended return. Common reasons for filing an amended return include:
- Incorrect income reporting
- Missed deductions or credits
- Changes in filing status
To file an amended return, use Form IT-255. Ensure all necessary documentation is included to avoid delays in processing.
Penalties for Late Payment
Avoiding Late Payment Penalties
Failing to pay your New York State income tax on time can result in penalties and interest charges. The penalty for late payment is typically 5% of the unpaid tax for each month or part of a month the tax remains unpaid, up to a maximum of 25%.
Interest is also charged on unpaid taxes, with the rate set by the state. To avoid these penalties, ensure you file and pay your taxes by the deadline or request an extension if needed.
Federal vs. State Tax Rates
Comparing Federal and State Taxes
While federal and state taxes are both important, they operate independently. Federal tax rates are generally higher than state rates, but they also offer more deductions and credits. New York State income tax percentage is designed to complement federal taxes, ensuring a balanced approach to taxation.
Understanding the differences between federal and state taxes can help you better plan your financial strategy and maximize your savings.
Using a New York State Tax Calculator
How to Use a Tax Calculator
A New York State tax calculator can simplify the process of estimating your tax liability. By entering your income, deductions, and credits, the calculator provides an estimate of your tax owed or refund due. This tool is especially useful for those who prefer to handle their taxes independently.
Several online calculators are available, including those provided by the New York State Department of Taxation and Finance. Ensure you use a reputable source to get accurate results.
Resources for Taxpayers
Where to Find Reliable Information
For more information on New York State income tax percentage, consider the following resources:
- New York State Department of Taxation and Finance
- IRS Publications and Guides
- Local Tax Professionals and Consultants
These resources offer comprehensive guidance and support for taxpayers navigating the complex world of state and federal taxes.
Conclusion and Next Steps
In conclusion, understanding New York State income tax percentage is vital for effective financial planning. By familiarizing yourself with the tax brackets, deductions, and credits available, you can optimize your tax strategy and minimize your liabilities.
We encourage you to take action by reviewing your tax situation, consulting with a tax professional if needed, and sharing this article with others who may benefit from the information. Together, we can ensure that all New York residents are well-informed about their tax obligations.
For further reading, explore our other articles on personal finance and tax planning. Your financial health is our priority!