New York State income tax rate is a critical financial consideration for individuals and businesses alike. Understanding how the tax brackets work, the various deductions available, and the overall impact on your finances is essential for effective tax planning. In this article, we will explore everything you need to know about New York State income tax rates, ensuring you stay informed and prepared for tax season.
New York is known for its high cost of living, and its income tax structure reflects that reality. Whether you're a resident earning a salary, a small business owner, or someone managing investments, knowing the intricacies of the state's tax system can help you save money and avoid potential pitfalls.
Our goal is to provide a detailed yet easy-to-understand guide that covers all aspects of New York State income tax rates. From the latest updates on tax brackets to expert advice on maximizing deductions, this article is your go-to resource for staying compliant and optimizing your financial strategy.
Read also:Alana Cho Of S Exploring Her Journey Achievements And Influence
Table of Contents
- Introduction to New York State Income Tax
- Understanding New York State Income Tax Brackets
- How Filing Status Affects Your Tax Rate
- Key Deductions and Credits for New York Taxpayers
- Tax Considerations for Self-Employed Individuals
- Business Income Tax in New York State
- Amended Returns and Refunds
- Penalties for Late Payment or Non-Compliance
- Comparing Federal vs. State Income Taxes
- Strategies for Effective Tax Planning
Introduction to New York State Income Tax
New York State income tax is a progressive tax system, meaning that the tax rate increases as your income increases. This structure ensures that higher earners contribute a larger percentage of their income to the state's revenue. The tax is administered by the New York State Department of Taxation and Finance, which provides resources and guidance for taxpayers.
In recent years, New York has implemented changes to its tax laws to address economic shifts and provide relief to certain groups, such as middle-income families and small businesses. Staying updated on these changes is crucial for accurate tax filing and planning.
For instance, the 2023 tax year introduced adjustments to the tax brackets to account for inflation, ensuring that taxpayers are not unfairly burdened by rising costs. These updates highlight the importance of understanding the nuances of New York's tax system.
Understanding New York State Income Tax Brackets
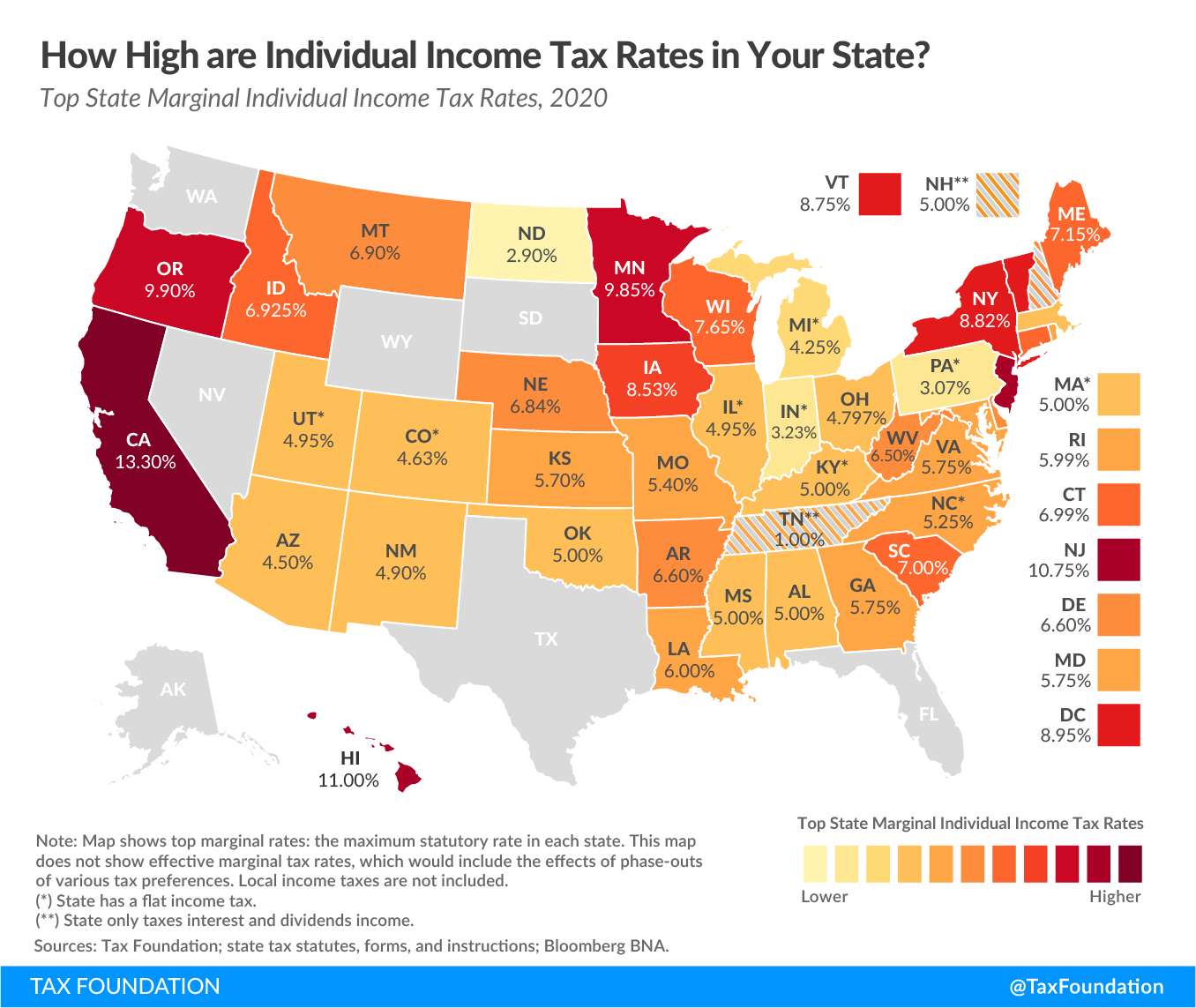
The New York State income tax brackets are divided into several tiers, each with its own tax rate. As of 2023, the brackets are as follows:
Income Tax Rates for Single Filers
- 4% on income up to $8,800
- 4.5% on income between $8,801 and $11,865
- 5.25% on income between $11,866 and $24,010
- 5.97% on income between $24,011 and $161,550
- 6.21% on income between $161,551 and $323,200
- 6.49% on income between $323,201 and $1,077,550
- 8.82% on income above $1,077,551
These brackets apply to single filers and head of household filers. Married couples filing jointly have slightly higher thresholds for each tier, reflecting their combined income.
How Filing Status Affects Your Tax Rate
Your filing status plays a significant role in determining your New York State income tax rate. The four main filing statuses are:
Read also:Leanne Morgan Daughters Unveiling The Lives And Achievements
- Single
- Married Filing Jointly
- Married Filing Separately
- Head of Household
Each status has its own set of tax brackets and deductions, so choosing the right one can impact your overall tax liability. For example, married couples filing jointly often benefit from higher income thresholds before reaching the higher tax brackets.
Consulting a tax professional or using tax software can help you determine the most advantageous filing status for your situation.
Key Deductions and Credits for New York Taxpayers
New York State offers several deductions and credits to help taxpayers reduce their taxable income. Some of the most common include:
Standard Deduction
All taxpayers are eligible for a standard deduction, which varies based on filing status. For 2023, the standard deduction for single filers is $8,800, while married couples filing jointly can claim $17,600.
Itemized Deductions
Taxpayers with significant expenses, such as mortgage interest or charitable contributions, may benefit from itemizing their deductions. This involves listing each deductible expense on Form IT-2105.
Additionally, New York offers credits for education expenses, childcare costs, and energy-efficient home improvements, among others. These credits can significantly lower your tax bill and are worth exploring during tax preparation.
Tax Considerations for Self-Employed Individuals
Self-employed individuals in New York face unique tax challenges. In addition to paying state income tax, they must also manage federal self-employment taxes, which include Social Security and Medicare contributions.
Estimated Tax Payments
Self-employed individuals are required to make quarterly estimated tax payments to avoid penalties. These payments should account for both state and federal taxes, ensuring compliance throughout the year.
Using a tax software or working with an accountant can simplify the process of calculating and submitting these payments. It's also important to keep detailed records of business expenses, as they can be deducted to reduce taxable income.
Business Income Tax in New York State
Businesses operating in New York State are subject to various taxes, including corporate income tax and franchise tax. The corporate income tax rate is currently 6.5%, with additional surcharges for businesses with higher profits.
Small Business Tax Relief
New York offers tax relief programs for small businesses, such as the Small Business Credit and the Start-Up NY initiative. These programs aim to reduce the financial burden on new and growing businesses, encouraging economic development across the state.
Business owners should consult with a tax advisor to ensure they are taking full advantage of available deductions and credits, as well as staying compliant with state and federal regulations.
Amended Returns and Refunds
Sometimes, taxpayers discover errors on their original tax return or experience changes in their financial situation that necessitate filing an amended return. New York State allows taxpayers to file Form IT-201X to correct errors or claim additional refunds.
Common reasons for filing an amended return include:
- Changes in marital status
- Updated income information
- Additional deductions or credits
It's important to file an amended return promptly to avoid potential penalties or delays in receiving refunds. The state typically processes amended returns within 12 weeks, but this timeline can vary depending on the complexity of the case.
Penalties for Late Payment or Non-Compliance
Failing to file or pay your New York State income taxes on time can result in significant penalties. The state imposes a late filing penalty of 5% of the unpaid tax for each month the return is late, up to a maximum of 25%. Additionally, a late payment penalty of 0.5% per month applies to unpaid balances.
In extreme cases, the state may take legal action to collect unpaid taxes, including wage garnishment or asset seizure. To avoid these consequences, taxpayers should prioritize timely filing and payment, even if they cannot pay the full amount owed.
Payment plans and extensions are available for those who need additional time to meet their tax obligations. Contacting the Department of Taxation and Finance can help you explore these options and avoid penalties.
Comparing Federal vs. State Income Taxes
While New York State income tax is progressive, the federal income tax system also follows a similar structure. However, there are key differences between the two that taxpayers should be aware of:
- Federal tax brackets are generally lower than state brackets, but they apply to a broader range of income.
- New York allows taxpayers to deduct federal income tax payments from their state taxable income.
- Certain deductions and credits are available at both the federal and state levels, but eligibility criteria may differ.
Coordinating federal and state tax strategies can lead to significant savings. For example, itemizing deductions on your federal return may also benefit your state return, depending on the specific expenses involved.
Strategies for Effective Tax Planning
Effective tax planning is essential for minimizing your tax liability and maximizing your financial resources. Here are some strategies to consider:
- Maximize Deductions: Take advantage of all available deductions, both standard and itemized, to reduce your taxable income.
- Utilize Tax-Deferred Accounts: Contributions to retirement accounts like IRAs or 401(k)s can lower your current tax bill while saving for the future.
- Stay Informed: Keep up with changes in tax laws and regulations, as they can impact your planning strategies.
- Consult a Professional: Working with a tax advisor or accountant can provide personalized guidance and ensure compliance with all applicable laws.
By implementing these strategies, you can optimize your tax situation and achieve greater financial stability.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding New York State income tax rates and regulations is vital for effective financial management. From navigating the progressive tax brackets to leveraging deductions and credits, staying informed and proactive can help you minimize your tax liability and maximize your savings.
We encourage you to share this article with others who may find it useful and leave a comment below if you have any questions or insights to add. For more information on New York State taxes and related topics, explore our other articles and resources. Together, we can ensure a brighter financial future for all taxpayers.