New York State income tax is an essential aspect of financial planning for residents and businesses within the state. Understanding how it works, its rates, exemptions, and filing requirements can significantly impact your financial health. Whether you're an individual taxpayer or a business owner, staying informed about New York's income tax regulations is crucial.
With one of the highest state tax rates in the country, New York's income tax system can be complex. However, by familiarizing yourself with its intricacies, you can ensure compliance and optimize your tax strategies. This guide will walk you through everything you need to know about New York State income tax.
From understanding the tax brackets to exploring deductions and credits, this article will provide a detailed overview to help you navigate the complexities of New York State income tax effectively. Let's dive in!
Read also:Discovering Daniel Radcliffe A Journey Through His Life And Career
Table of Contents
- Introduction to New York State Income Tax
- Understanding New York State Income Tax Brackets
- Filing Status and Requirements
- Exploring Deductions and Credits
- Personal and Dependent Exemptions
- Business Income Tax in New York State
- Recent Amendments and Updates
- The Filing Process: Step-by-Step Guide
- Penalties for Late or Incorrect Filing
- Resources for Taxpayers
- Conclusion and Call to Action
Introduction to New York State Income Tax
New York State income tax is levied on the income of individuals, corporations, and other entities that earn income within the state. The tax is progressive, meaning that higher income levels are taxed at higher rates. This system ensures that those who earn more contribute a fair share to the state's revenue.
The New York State Department of Taxation and Finance oversees the collection and administration of income taxes. Taxpayers must file their returns annually, typically by April 15th, unless an extension is granted. Understanding the nuances of the tax system is essential for both individuals and businesses to avoid penalties and optimize their financial planning.
Understanding New York State Income Tax Brackets
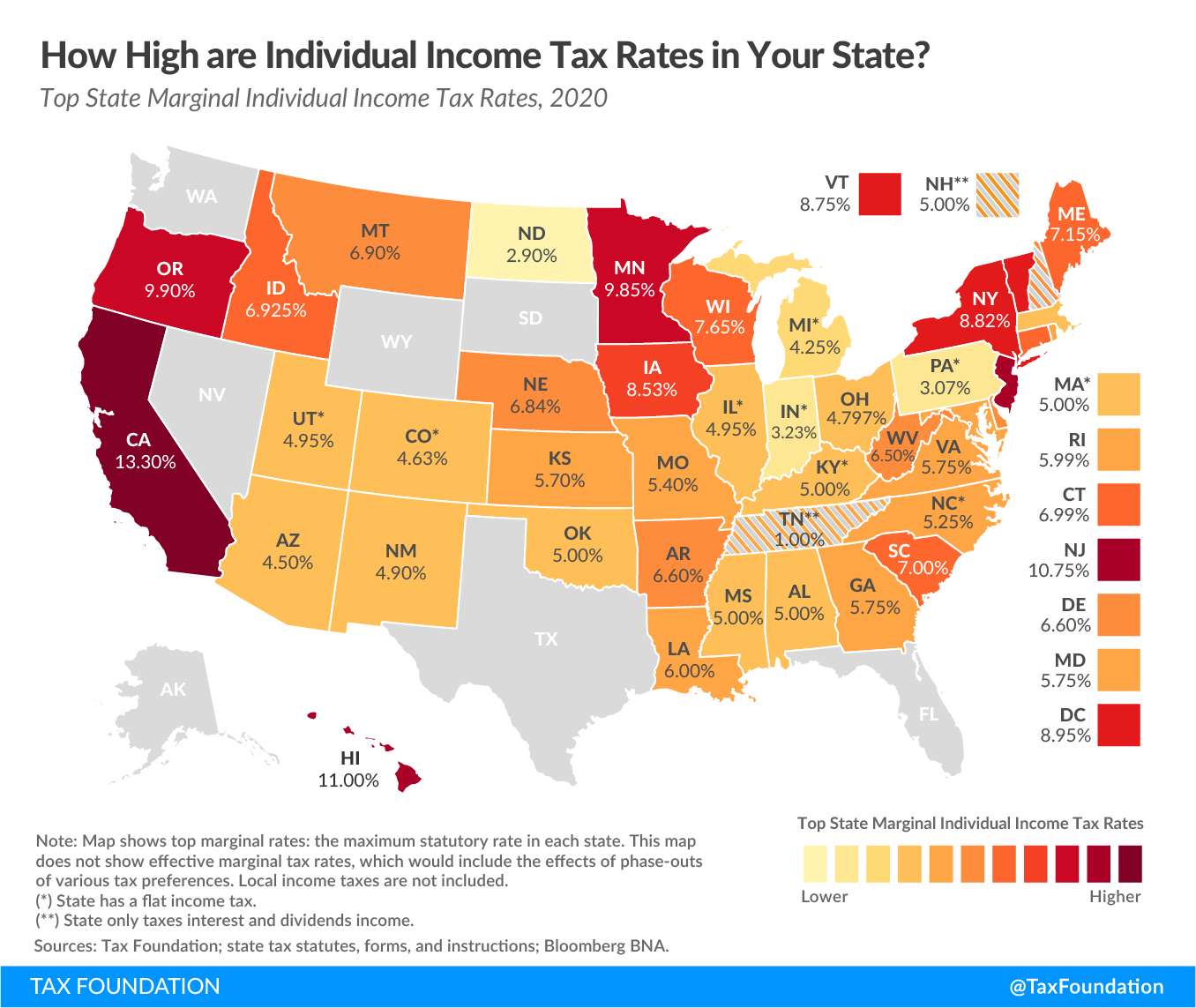
New York State income tax is structured into several brackets, each with a corresponding tax rate. These brackets are designed to ensure that taxpayers are taxed fairly based on their income level.
Tax Rates and Brackets
- For incomes up to $8,500: Tax rate of 4%
- For incomes between $8,501 and $11,700: Tax rate of 4.5%
- For incomes between $11,701 and $13,900: Tax rate of 5.25%
- For incomes between $13,901 and $21,800: Tax rate of 5.97%
- For incomes over $21,800: Tax rate increases progressively up to 8.82% for the highest earners
These brackets are subject to change based on legislative updates and inflation adjustments. It's important for taxpayers to stay updated on the latest rates to ensure accurate filings.
Filing Status and Requirements
Taxpayers in New York State must determine their filing status to ensure they are filing correctly. The most common filing statuses include single, married filing jointly, married filing separately, and head of household.
Key Considerations for Filing
- Single Filers: Individuals who are unmarried or legally separated as of December 31st.
- Married Filing Jointly: Married couples filing a single return together.
- Married Filing Separately: Married couples choosing to file separate returns.
- Head of Household: Unmarried taxpayers who pay more than half the cost of maintaining a home for themselves and a qualifying person.
Each status has its own set of requirements and benefits, so it's important to choose the one that best fits your situation.
Read also:Jacob Colliers Wife A Deep Dive Into His Personal Life And Musical Journey
Exploring Deductions and Credits
New York State offers various deductions and credits to help reduce the tax burden on individuals and businesses. These include standard deductions, itemized deductions, and specific credits tailored to different taxpayer needs.
Common Deductions and Credits
- Standard Deduction: A fixed amount that taxpayers can subtract from their income.
- Itemized Deductions: Specific expenses such as mortgage interest, charitable contributions, and medical expenses that can be deducted.
- Child Tax Credit: A credit available for taxpayers with qualifying children.
- Education Credits: Credits for tuition and related expenses for higher education.
Taking advantage of these deductions and credits can significantly lower your taxable income and overall tax liability.
Personal and Dependent Exemptions
Personal and dependent exemptions allow taxpayers to reduce their taxable income by a specific amount for themselves and each dependent they claim. While the federal government has eliminated personal exemptions, New York State still offers them to its residents.
Eligibility for Exemptions
- Personal Exemption: Available to taxpayers who are not claimed as dependents on another person's tax return.
- Dependent Exemption: Available for qualifying dependents, including children and certain relatives.
These exemptions are subject to income limits, so it's important to verify eligibility based on your income level.
Business Income Tax in New York State
Businesses operating in New York State are also subject to income tax, with rates and regulations that differ from individual taxpayers. Understanding these requirements is crucial for businesses to remain compliant and manage their tax liabilities effectively.
Key Business Tax Considerations
- Corporate Income Tax: Applies to corporations with a flat tax rate of 6.5%.
- Pass-Through Entities: Partnerships and S-corporations pass their income to owners, who then pay individual income tax.
- Franchise Tax: Additional tax imposed on corporations based on net worth or income.
Businesses must also consider local taxes and other fees that may apply depending on their location and industry.
Recent Amendments and Updates
Legislative changes and updates frequently affect New York State income tax regulations. Staying informed about these changes is essential for taxpayers to ensure compliance and take advantage of new benefits.
Notable Updates
- Tax Rate Adjustments: Recent updates have adjusted tax rates for certain income brackets.
- New Credits and Deductions: Introduction of new credits to support specific taxpayer groups.
- Extension of Deadlines: Temporary extensions due to unforeseen circumstances such as natural disasters or pandemics.
Regularly checking updates from the New York State Department of Taxation and Finance is recommended to stay informed.
The Filing Process: Step-by-Step Guide
Filing your New York State income tax return can seem daunting, but following a step-by-step process can make it manageable. Here's a guide to help you through the process:
Steps to File Your Return
- Gather all necessary documents, including W-2s, 1099s, and receipts for deductions.
- Choose your filing status and calculate your taxable income.
- Claim applicable deductions and credits to reduce your tax liability.
- Submit your return electronically or via mail by the deadline.
Using tax software or consulting a tax professional can simplify the process and ensure accuracy.
Penalties for Late or Incorrect Filing
Failing to file your New York State income tax return on time or making errors in your filing can result in penalties and interest charges. Understanding these consequences can motivate taxpayers to prioritize timely and accurate filings.
Potential Penalties
- Failure to File Penalty: 5% of the tax owed for each month the return is late, up to a maximum of 25%.
- Failure to Pay Penalty: 0.5% of the tax owed for each month the payment is late, up to a maximum of 25%.
- Interest Charges: Interest is charged on unpaid taxes at the federal short-term rate plus 2%.
Avoiding these penalties is crucial for maintaining financial stability and avoiding unnecessary expenses.
Resources for Taxpayers
New York State provides various resources to assist taxpayers in understanding and fulfilling their tax obligations. These resources include online tools, publications, and support from tax professionals.
Available Resources
- New York State Department of Taxation and Finance Website: Offers forms, instructions, and updates on tax regulations.
- Free Tax Preparation Services: Available for low-to-moderate-income individuals through volunteer programs.
- Tax Professional Consultation: Professional advice from certified public accountants or tax attorneys.
Utilizing these resources can enhance your understanding and simplify the tax filing process.
Conclusion and Call to Action
New York State income tax is a critical component of financial planning for residents and businesses. By understanding the tax brackets, deductions, credits, and filing requirements, taxpayers can ensure compliance and optimize their tax strategies. Staying informed about recent updates and utilizing available resources is key to managing your tax obligations effectively.
We encourage you to share this article with others who may find it helpful and leave a comment below if you have any questions or additional insights. For more information on tax-related topics, explore our other articles and resources. Remember, staying informed is the first step toward financial success!