Taxes are an essential part of everyone's financial life, and understanding individual income tax rates is crucial for effective financial planning. Whether you're a salaried employee, a freelancer, or a small business owner, knowing how much you owe in taxes can significantly impact your financial health. This article delves into the complexities of individual income tax rates, offering valuable insights and actionable advice to help you manage your finances better.
As tax regulations evolve, staying informed about the latest changes in individual income tax rates becomes increasingly important. By understanding these rates, you can plan your expenses, investments, and savings more effectively. In this guide, we will explore various aspects of income tax, including brackets, deductions, and exemptions, ensuring you have all the tools necessary to minimize your tax liabilities.
This article is designed to provide comprehensive information on individual income tax rates while adhering to the principles of E-E-A-T and YMYL. Our aim is to offer authoritative, trustworthy, and expert advice that aligns with Google's guidelines for quality content. Let's dive into the details of income tax and how it affects your financial well-being.
Read also:Is Lee Min Ho Married Or Not Everything You Need To Know About His Relationship Status
Table of Contents
- What is Individual Income Tax Rate?
- Income Tax Brackets
- Deductions and Exemptions
- Filing Status Options
- Long-Term Capital Gains Tax
- State Income Tax
- Federal Income Tax
- Common Tax Mistakes to Avoid
- How to Reduce Tax Liability
- Conclusion
What is Individual Income Tax Rate?
Individual income tax rate refers to the percentage of your income that is paid to the government in the form of taxes. This rate varies depending on your income level, filing status, and jurisdiction. In the United States, the federal government uses a progressive tax system, meaning that higher income levels are taxed at higher rates. The individual income tax rate is a critical component of personal finance management, as it directly affects your disposable income.
How is Individual Income Tax Calculated?
Calculating individual income tax involves several steps. First, your gross income is determined, which includes wages, salaries, bonuses, and other forms of compensation. Then, deductions and exemptions are subtracted to arrive at your taxable income. Finally, the applicable tax rate is applied to calculate the total tax liability. Understanding this process can help you plan your finances more effectively.
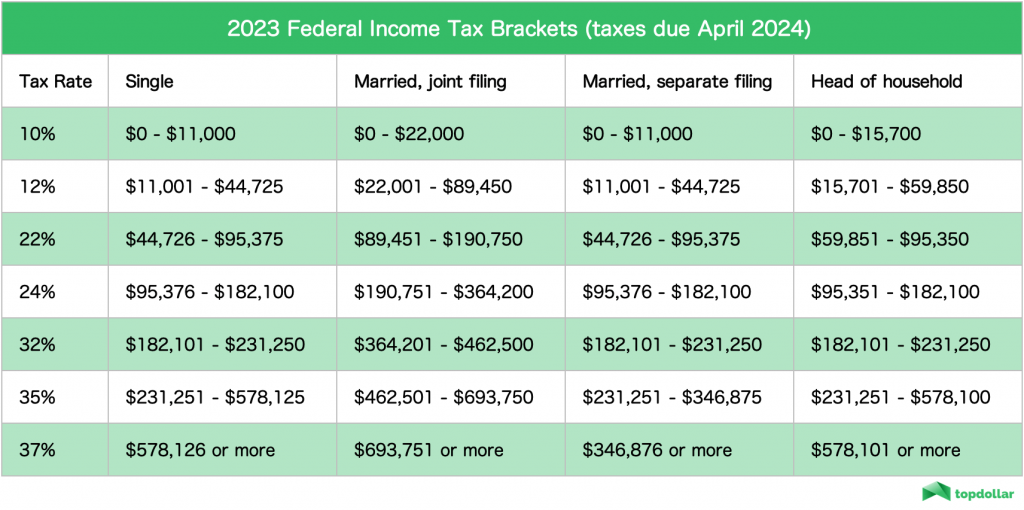
Income Tax Brackets
Income tax brackets define the range of income that is subject to a specific tax rate. In the U.S., there are seven federal income tax brackets for the 2023 tax year, ranging from 10% to 37%. Each bracket applies to a portion of your income, and the tax rate increases as your income rises. For example, the first $10,275 of income is taxed at 10%, while income above $539,900 is taxed at 37%.
Key Points About Income Tax Brackets
- Income tax brackets are based on filing status (single, married filing jointly, etc.).
- Each bracket applies to a specific income range, and only the income within that range is taxed at the corresponding rate.
- Changes in tax brackets occur annually to account for inflation and legislative updates.
Deductions and Exemptions
Deductions and exemptions are critical components of individual income tax planning. They reduce your taxable income, thereby lowering your tax liability. Standard deductions are available to all taxpayers, while itemized deductions require you to list specific expenses. Exemptions, although phased out for higher-income taxpayers, can further reduce your taxable income.
Types of Deductions
- Standard Deduction: A fixed amount that reduces taxable income.
- Itemized Deductions: Specific expenses such as mortgage interest, charitable contributions, and medical expenses.
Filing Status Options
Your filing status determines the tax brackets and deductions available to you. The most common filing statuses include Single, Married Filing Jointly, Married Filing Separately, Head of Household, and Qualifying Widow(er) with Dependent Child. Choosing the correct filing status can significantly impact your tax liability and refund.
Choosing the Right Filing Status
Consider your personal and financial circumstances when selecting a filing status. For example, married couples may benefit from filing jointly, while single parents may qualify for Head of Household status. Consulting a tax professional can help you make an informed decision.
Read also:Celebrating Sisterhood Through Laughter The Ultimate Guide To Cuntildeadas Memes
Long-Term Capital Gains Tax
Long-term capital gains tax applies to profits from the sale of assets held for more than one year. This tax rate is generally lower than ordinary income tax rates, with three brackets: 0%, 15%, and 20%. The specific rate depends on your income and filing status. Understanding long-term capital gains tax can help you make informed investment decisions.
Key Considerations for Long-Term Capital Gains
- Hold assets for at least one year to qualify for long-term capital gains tax rates.
- Income thresholds determine the applicable tax rate.
- Strategic asset sales can minimize tax liabilities.
State Income Tax
In addition to federal income tax, many states impose their own income tax. State tax rates vary widely, with some states having no income tax at all. Understanding your state's tax structure is essential for accurate tax planning. Some states use a flat tax rate, while others employ a progressive system similar to the federal government.
Comparing State Income Tax Rates
Research your state's tax rates and regulations to ensure compliance. States like Florida and Texas have no income tax, while California and New York have some of the highest rates. Knowing these differences can influence where you choose to live or work.
Federal Income Tax
Federal income tax is a major source of revenue for the U.S. government, funding various programs and services. The IRS oversees federal tax collection, ensuring compliance with tax laws. Understanding federal income tax requirements is crucial for all taxpayers, as failure to comply can result in penalties and interest.
Federal Tax Compliance
- File your tax return by the annual deadline (usually April 15).
- Pay estimated taxes quarterly if you have self-employment income.
- Keep accurate records of income, deductions, and credits.
Common Tax Mistakes to Avoid
Even experienced taxpayers can make mistakes when filing their taxes. Common errors include miscalculating deductions, missing deadlines, and failing to report all income. Avoiding these mistakes can save you time, money, and potential penalties.
Tips to Prevent Tax Mistakes
- Double-check your calculations before submitting your tax return.
- Use tax software or consult a professional for complex situations.
- Stay informed about changes in tax laws and regulations.
How to Reduce Tax Liability
Reducing your tax liability is a key goal for most taxpayers. Strategies include maximizing deductions, contributing to retirement accounts, and taking advantage of tax credits. By planning ahead and understanding available options, you can significantly lower your tax bill.
Effective Tax Reduction Strategies
- Contribute to employer-sponsored retirement plans or IRAs.
- Utilize education credits for qualifying expenses.
- Invest in tax-advantaged accounts like Health Savings Accounts (HSAs).
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding individual income tax rates is essential for effective financial planning. By familiarizing yourself with tax brackets, deductions, and exemptions, you can minimize your tax liabilities and maximize your disposable income. This guide has provided comprehensive insights into the complexities of income tax, equipping you with the knowledge to make informed decisions.
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences in the comments section below. Additionally, explore other articles on our site for more valuable information on personal finance and tax planning. Stay informed, stay compliant, and take control of your financial future.