New York State TA income is a crucial topic for both residents and non-residents who earn income within the state. Whether you're a part-time worker, freelancer, or someone employed by a company, understanding how New York State taxes your income is essential for financial planning and compliance. This guide aims to demystify everything you need to know about NY State TA income.
Taxation rules in New York can be complex, especially when it comes to determining taxable income. With various factors such as residency status, deductions, and credits affecting your tax liability, staying informed is key. This article will explore the intricacies of NY State TA income and provide actionable insights to help you manage your finances effectively.
Whether you're looking to understand how your income is taxed, what deductions you qualify for, or how to file your taxes accurately, this guide is designed to answer all your questions. Let's dive into the world of NY State TA income and equip you with the knowledge you need to navigate the tax system confidently.
Read also:Understanding The Power Of Ing How It Shapes Language And Communication
Table of Contents
- Introduction to NY State TA Income
- Determining Tax Residency in New York State
- Types of Income Taxed in NY State
- NY State Tax Rates Explained
- Filing Status Options for NY Residents
- Deductions and Credits Available
- The NY State Income Tax Filing Process
- Understanding Penalties and Interest
- Useful Resources for NY Taxpayers
- Conclusion and Next Steps
Introduction to NY State TA Income
When it comes to taxation, New York State has a reputation for being one of the more complex jurisdictions in the United States. NY State TA income refers to the portion of your earnings that are subject to state taxation. This includes wages, salaries, tips, and other forms of compensation earned within the state.
Why Understanding NY State TA Income Matters
For many taxpayers, NY State TA income is a significant financial consideration. The state's progressive tax system means that higher earners may face a heavier tax burden. Understanding how your income is taxed can help you make informed decisions about saving, investing, and spending.
In addition to income tax, New York State also imposes various other taxes, such as sales tax, property tax, and excise tax. However, this guide focuses specifically on income taxation, providing you with the tools you need to manage your tax obligations effectively.
Determining Tax Residency in New York State
Your tax residency status plays a critical role in determining how much of your income is subject to NY State TA income taxes. New York State recognizes two types of residents for tax purposes: residents and nonresidents.
Read also:Exploring Travel Options Greyhound Bus Cleveland
Resident Taxpayers
A resident taxpayer is someone who maintains a permanent place of abode in New York State and spends more than 183 days of the year within the state. Resident taxpayers are required to report all their income, regardless of where it was earned, on their NY State tax return.
Nonresident Taxpayers
Nonresident taxpayers are individuals who do not meet the residency criteria but still earn income within New York State. Nonresidents are only required to report the income they earn from New York-based sources, such as wages from a job located in the state.
Types of Income Taxed in NY State
NY State TA income encompasses a wide range of earnings. Below are the most common types of income subject to taxation:
- Wages, salaries, and tips
- Self-employment income
- Interest and dividends
- Rental income
- Capital gains
- Unemployment compensation
It's important to note that certain types of income, such as Social Security benefits, may be partially or fully exempt from taxation depending on your circumstances.
NY State Tax Rates Explained
New York State uses a progressive tax system, meaning that higher income levels are taxed at higher rates. As of the latest tax year, the state tax brackets range from 4% for lower-income taxpayers to 8.82% for those in the highest bracket.
How Tax Rates Affect You
Your effective tax rate will depend on your total taxable income and the deductions and credits you qualify for. For example, if you earn $50,000 annually and qualify for several deductions, your taxable income may be significantly lower, resulting in a reduced tax liability.
For the most accurate information, consult the New York State Department of Taxation and Finance website or seek advice from a tax professional.
Filing Status Options for NY Residents
Choosing the correct filing status is essential for ensuring accurate tax reporting. New York State recognizes several filing statuses, including:
- Single
- Married filing jointly
- Married filing separately
- Head of household
Selecting the Right Filing Status
Your filing status will impact your tax bracket, standard deduction, and eligibility for certain credits. For instance, married couples filing jointly may benefit from lower tax rates and increased deduction limits compared to filing separately.
It's important to evaluate your financial situation carefully when selecting a filing status. Consulting with a tax advisor can help you make the best decision for your unique circumstances.
Deductions and Credits Available
NY State TA income tax calculations can be significantly influenced by the deductions and credits you claim. Below are some of the most common deductions and credits available to New York taxpayers:
- Standard deduction
- Itemized deductions
- Child tax credit
- Earned income tax credit
- Educational credits
Maximizing Your Deductions and Credits
To maximize your deductions and credits, keep detailed records of your expenses throughout the year. This includes receipts, invoices, and any other documentation that supports your claims. By doing so, you can ensure that you take full advantage of all available tax benefits.
The NY State Income Tax Filing Process
Filing your NY State TA income tax return is a straightforward process if you have all the necessary information. Here's a step-by-step guide to help you through the process:
- Gather all required documents, including W-2 forms, 1099 forms, and any other relevant paperwork.
- Choose your filing method: online or paper filing.
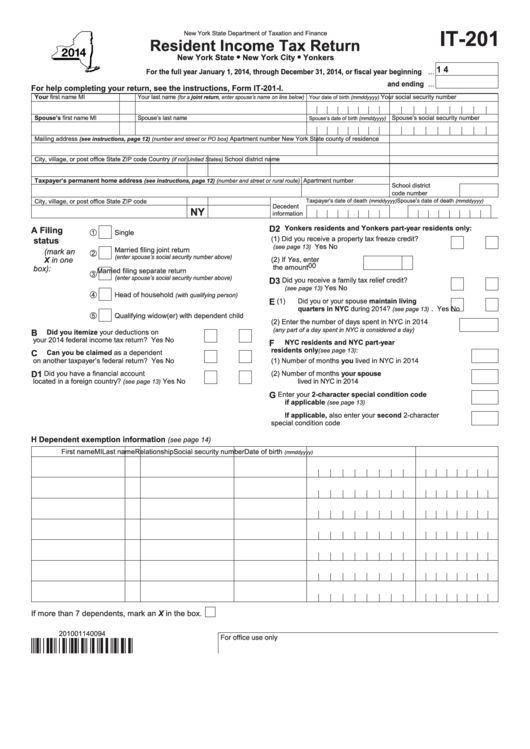
- Complete Form IT-201, the New York State Resident Income Tax Return, or Form IT-203, the Nonresident and Part-Year Resident Income Tax Return.
- Review your return carefully for accuracy before submitting it.
- Pay any taxes owed or request a refund if applicable.
Tips for a Smooth Filing Experience
File your tax return early to avoid last-minute stress and potential penalties. Use tax preparation software or consult with a tax professional if you're unsure about any aspect of the process. Keeping your records organized throughout the year will also make filing much easier.
Understanding Penalties and Interest
Failing to file your NY State TA income tax return on time or paying the correct amount of taxes can result in penalties and interest. The penalties vary depending on the severity of the infraction, but they can include:
- Failure-to-file penalty
- Failure-to-pay penalty
- Underpayment penalty
Avoiding Penalties and Interest
To avoid penalties and interest, make sure to file your tax return by the deadline and pay any taxes owed on time. If you're unable to meet the deadline, file for an extension and pay an estimated amount of your tax liability to avoid additional charges.
Useful Resources for NY Taxpayers
Several resources are available to help New York taxpayers navigate the complexities of NY State TA income taxation. Below are some of the most valuable resources:
- New York State Department of Taxation and Finance website
- IRS website for federal tax information
- Tax preparation software such as TurboTax or H&R Block
- Local tax professionals and accountants
Staying Informed
Tax laws and regulations are subject to change, so staying informed is crucial. Regularly check the official New York State tax website for updates and subscribe to newsletters or alerts to receive the latest information directly.
Conclusion and Next Steps
Understanding NY State TA income is vital for ensuring compliance with tax laws and optimizing your financial well-being. By familiarizing yourself with the key concepts covered in this guide, you can make informed decisions about your taxes and take advantage of available deductions and credits.
We encourage you to take the following steps:
- Review your tax situation and gather all necessary documents.
- Consult with a tax professional if you have complex tax needs.
- File your tax return accurately and on time to avoid penalties.
Share this article with others who may find it helpful and explore our other resources for more information on personal finance and taxation. Together, let's ensure you're well-prepared for the tax season and beyond.