Communication is a fundamental aspect of human interaction, and within this process, hearing plays a crucial role. Hearing definition in communication goes beyond simply detecting sound; it involves the ability to interpret and understand auditory information effectively. In today's fast-paced world, effective communication is essential for personal and professional success, making it imperative to explore the nuances of hearing in communication.
Hearing is not just a passive process but an active skill that requires attention, focus, and comprehension. As we delve deeper into this topic, you'll discover how hearing impacts communication, the challenges associated with it, and strategies to enhance auditory understanding. Whether you're a student, professional, or simply interested in improving your communication skills, this article will provide valuable insights.
In addition to exploring the technical aspects of hearing, we will also examine its psychological and social dimensions. By understanding the hearing definition in communication, you can improve your ability to connect with others, resolve conflicts, and build stronger relationships. Let's explore this fascinating topic together!
Read also:His Paternal Lineage Vedang Rainarsquos Fatherrsquos Influence
Table of Contents
- Defining Hearing in Communication
- The Importance of Hearing in Communication
- The Process of Hearing
- Common Challenges in Hearing
- Hearing Loss and Its Impact
- Effective Listening Techniques
- Technology's Role in Enhancing Hearing
- Social Implications of Hearing in Communication
- Psychological Aspects of Hearing
- Conclusion and Call to Action
Defining Hearing in Communication
Hearing is the physiological process by which sound waves are captured, processed, and interpreted by the auditory system. In communication, hearing serves as the foundation for understanding spoken language, environmental sounds, and emotional cues. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), approximately 430 million people worldwide suffer from hearing loss, underscoring the importance of addressing this issue.
The hearing definition in communication extends beyond mere sound detection. It involves active listening, comprehension, and the ability to respond appropriately. This skill is crucial in both verbal and non-verbal communication, enabling individuals to engage meaningfully with others.
The Importance of Hearing in Communication
Hearing plays a vital role in shaping our interactions with the world around us. In communication, it allows us to perceive and interpret spoken words, tones, and nuances. Effective hearing enhances our ability to form connections, resolve misunderstandings, and collaborate with others. For instance, in professional settings, good hearing ensures that important instructions and feedback are not missed.
Moreover, hearing contributes to emotional intelligence by enabling individuals to recognize subtle changes in tone and pitch. This ability is particularly important in interpersonal relationships, where empathy and understanding are key to resolving conflicts and building trust.
The Process of Hearing
The process of hearing involves a complex interplay between the auditory system and the brain. Sound waves are captured by the outer ear, travel through the ear canal, and vibrate the eardrum. These vibrations are then transmitted to the middle ear, where tiny bones amplify the sound before it reaches the inner ear.
The Auditory System
The auditory system is composed of several key components, including the outer ear, middle ear, and inner ear. Each part plays a specific role in processing sound. For example, the cochlea in the inner ear converts sound waves into electrical signals, which are then sent to the brain for interpretation. Damage to any part of this system can lead to hearing impairments.
Read also:Is Rosey Grier Still Alive Discover The Life And Legacy Of The Nfl Legend
Brain's Role in Interpretation
Once the electrical signals reach the brain, they are processed in the auditory cortex. This area is responsible for decoding the signals into meaningful information, such as words, music, and environmental sounds. The brain also helps distinguish between relevant and irrelevant sounds, allowing us to focus on important conversations even in noisy environments.
Common Challenges in Hearing
Despite its importance, hearing is not without its challenges. Factors such as noise pollution, aging, and medical conditions can negatively impact auditory function. For example, prolonged exposure to loud noises can lead to noise-induced hearing loss, a condition that affects millions of people globally.
Other common challenges include difficulty distinguishing sounds in crowded environments, difficulty following fast-paced conversations, and misinterpreting spoken words. These issues can hinder effective communication and lead to frustration for both parties involved.
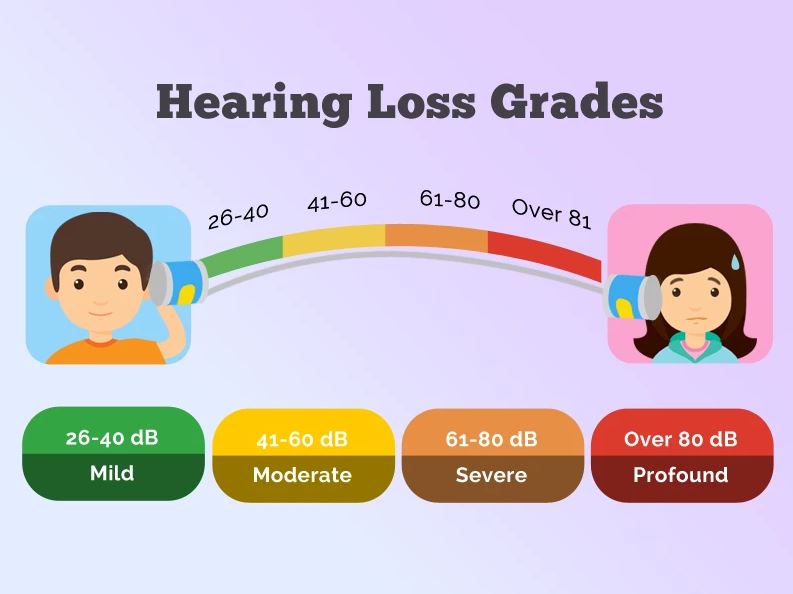
Hearing Loss and Its Impact
Hearing loss is a growing concern worldwide, with significant implications for communication and quality of life. It can result from a variety of factors, including genetic predisposition, infections, and environmental factors.
Types of Hearing Loss
There are three main types of hearing loss: conductive, sensorineural, and mixed. Conductive hearing loss occurs when sound waves are unable to travel efficiently through the outer or middle ear. Sensorineural hearing loss, on the other hand, involves damage to the inner ear or auditory nerve. Mixed hearing loss combines elements of both conductive and sensorineural impairments.
Prevention and Treatment Options
Preventing hearing loss involves adopting protective measures, such as wearing earplugs in noisy environments and avoiding excessive exposure to loud sounds. Treatment options for hearing loss include hearing aids, cochlear implants, and auditory rehabilitation programs. These interventions can significantly improve auditory function and enhance communication abilities.
Effective Listening Techniques
Effective listening is a skill that can be developed through practice and awareness. Some techniques for improving listening include:
- Minimizing distractions during conversations
- Maintaining eye contact with the speaker
- Asking clarifying questions to ensure understanding
- Practicing active listening by summarizing key points
By incorporating these techniques into your daily interactions, you can improve your ability to hear and understand others, leading to more productive and fulfilling communication experiences.
Technology's Role in Enhancing Hearing
Advances in technology have revolutionized the field of audiology, offering innovative solutions for individuals with hearing impairments. Modern hearing aids, for example, are equipped with features such as noise cancellation, directional microphones, and Bluetooth connectivity. These devices enhance auditory function by amplifying sound and reducing background noise.
In addition to hearing aids, cochlear implants provide a viable option for individuals with severe hearing loss. These devices bypass damaged parts of the auditory system, delivering electrical signals directly to the brain. With ongoing research and development, the future of hearing technology looks promising.
Social Implications of Hearing in Communication
Hearing plays a critical role in social interactions, influencing how we perceive and engage with others. Individuals with hearing impairments may experience social isolation, reduced self-esteem, and difficulty forming relationships. Addressing these challenges requires a combination of technological solutions, social support, and public awareness.
By promoting inclusive communication practices, such as using visual aids and sign language, we can create environments that accommodate diverse auditory needs. This approach not only benefits individuals with hearing impairments but also enriches the overall communication experience for everyone involved.
Psychological Aspects of Hearing
Hearing is closely linked to psychological well-being, affecting emotions, cognition, and behavior. For example, individuals with hearing impairments may experience increased stress and anxiety due to difficulties in communication. Conversely, good hearing contributes to emotional resilience, enabling individuals to navigate social situations with confidence.
Research has shown that auditory stimulation can enhance cognitive function, particularly in older adults. Activities such as listening to music, engaging in conversations, and participating in group discussions can help maintain mental sharpness and prevent cognitive decline.
Conclusion and Call to Action
In conclusion, the hearing definition in communication encompasses more than just sound detection; it involves active listening, comprehension, and emotional engagement. By understanding the importance of hearing and addressing common challenges, we can improve our communication skills and build stronger connections with others.
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences in the comments section below. Have you encountered any specific challenges related to hearing in communication? What strategies have you found effective in overcoming these obstacles? Additionally, feel free to explore other articles on our site for more insights into communication and personal development.